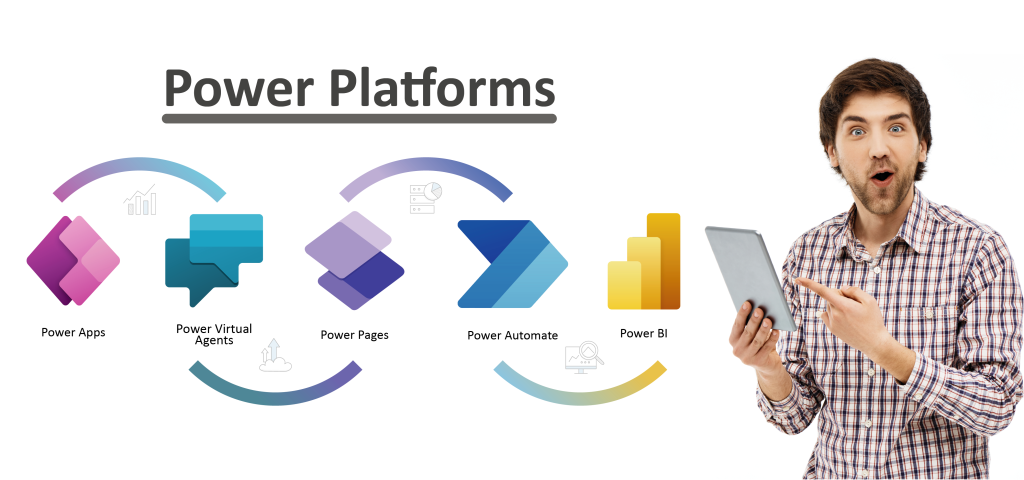
Power Platform with Power BI as a Data Analysis and Visualization Tool
The Microsoft 365 ecosystem is gaining more strength every day in the corporate context and behind this there is a great integrating platform of Low Code applications that transparently allow connectivity, security and total integration. Similarly, the possibility of using machine learning and artificial intelligence capabilities available to Microsoft, makes this suite even more robust, which currently consists of the following tools:
Power Apps
Power Apps is a Microsoft platform that allows users to create custom business applications without programming skills. You can use pre-built templates or create your own apps using a drag-and-drop interface, and connect them to different data sources such as Excel, SharePoint, Dynamics 365 and more. With Power Apps, you can create applications to automate business processes, improve collaboration and decision making, and access your data from anywhere on any device.
Virtual Agents:
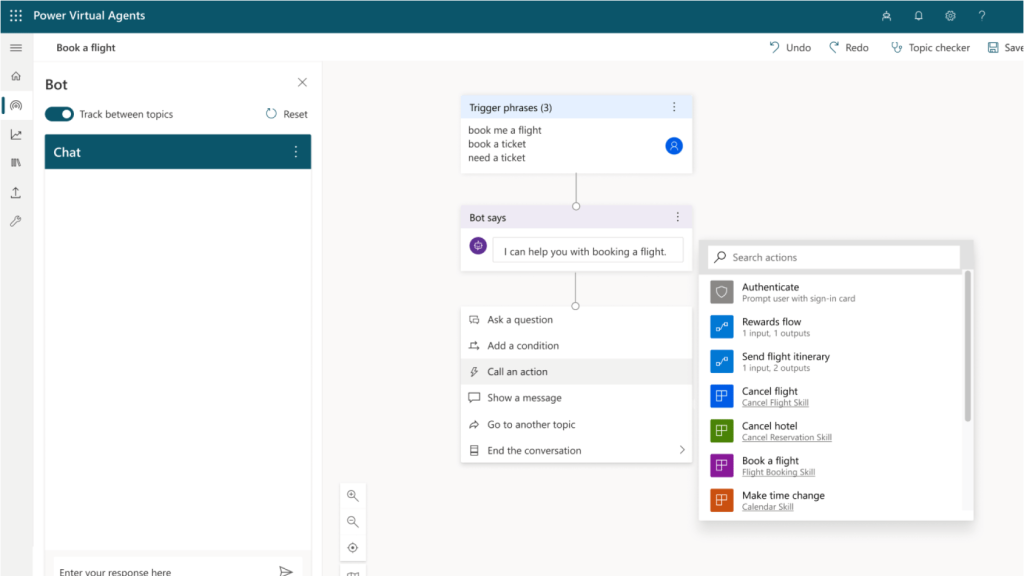
It allows you to create virtual agents or chatbots to automate customer service and resolve frequently asked questions. Virtual agents are computer programs designed to simulate a conversation with users through a chat or voice interface.
With Virtual Agents, you can create a virtual agent with a drag-and-drop interface, without programming skills; customize the virtual agent’s dialog to answer specific questions and provide accurate information; and connect the virtual agent to different data sources for real-time information.
Virtual agents can be implemented in different channels such as websites, mobile applications, social networks, among others, and offer an automated way to interact with customers and provide information quickly and efficiently.
Power Pages:
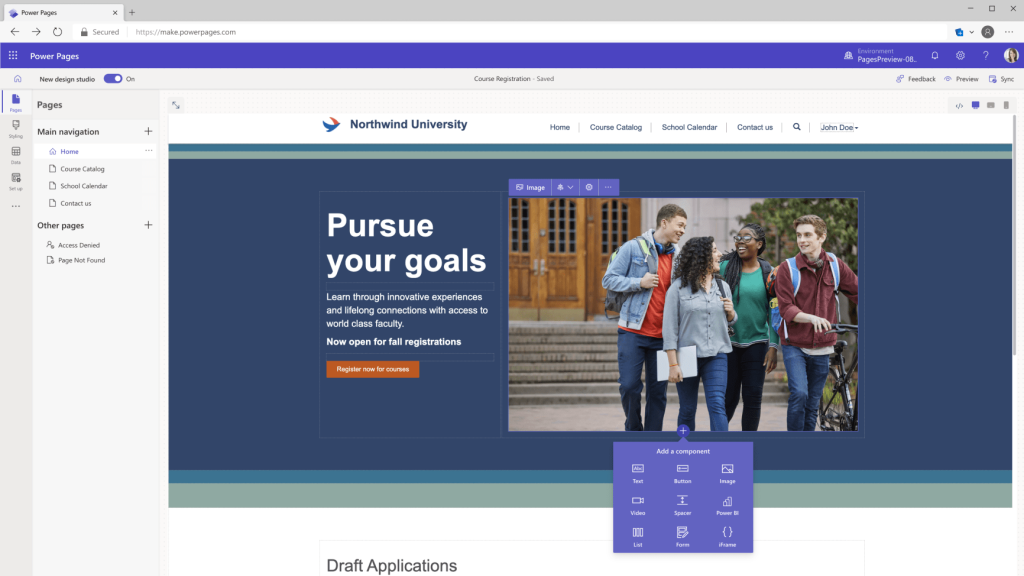
Power Pages is another of the new Microsoft Power Platform tools, which allows you to create and customize web pages quickly by dragging and dropping. These pages can be used to display information, such as data from a database or to integrate with other applications, such as Dynamics 365 or SharePoint. Power Pages also allows you to create forms and web applications without having to learn to program.
Power Automate:
Automate tasks and business processes by creating workflows. With Power Automate, you can connect different applications and services, such as Outlook, SharePoint, Dynamics 365, among others, and create automated workflows that are triggered when certain conditions are met. For example, you could create a workflow that sends an email automatically every time a new item is added to a SharePoint list, or creates a new task in your calendar when a specific email is received.
Power Automate has a drag-and-drop interface that allows you to create workflows without having to write code. You can use pre-built templates to start creating your workflows or create your own workflows from scratch.
Power BI:
Last but not least, we have the Business Intelligence tool Power BI, with which you can perform data analysis, create reports and dashboards in a visual way. Similarly, it allows you to connect data from different sources, such as Excel, SQL Server or a database in the cloud, and create graphs and tables that help to better understand the data. In addition, Power BI has a number of advanced features, such as integration with Power Automate, which allows you to automate processes by creating workflows, and the use of custom data models to analyze data more accurately.
Another major advantage of Power BI is its integration with day-to-day tools in Microsoft 365, such as Excel and SharePoint. You can import data from Excel into Power BI, then create interactive visualizations and share them easily on a SharePoint page. In addition, you can use Power BI to create custom reports and integrate them into applications and websites.
With all the above mentioned and without this being a detailed article of everything that can be achieved with Power Platform, we can summarize that, with this combination of tools, users get to develop flexible and scalable solutions for the company, without necessarily having advanced knowledge of development.
In later articles I will address some of these tools in particular to show how you can adopt them in your business and what benefits you might gain.
Author:
Juan Gabriel Sánchez
Project Manager




